Hello Students, in this article I am going to provide Financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes for Free.
These notes are very easy to read and understand and if you want to read these notes once so, you will understand the complete chapter in a few minutes.
So without wasting any time. Let’s get started with our notes on this awesome chapter titled: Cleaning, Settlements, and Legal Frameworks.
At the starting of the notes, we will tell you about the basic terms that are included in the title of chapter 3.
Clearing, Settlement and Legal Framework: financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes
In this chapter, we will talk about how the trade is being settled by the broker after it was executed by the buyer in the whole transfer of money from the buyer’s account to the seller’s account and securities from the seller’s account to the buyer’s account is done through a procedure that involves some legal framework too.
The complete procedure is done by the broker and this complete process of settlement and clearing includes the use of a state of art information technology, emergency of clearing corporations to assume counterparty risk, dematerialization, shorter settlement cycle, electronic or online transfer of securities, fine-tuned risk management system.
We hope that this financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes are going to be very helpful for you.
What is Clearing?
The clearing is a kind of financial marketing settlement that includes the transfer of funds to the seller and securities to the buyer.
What is Settlement?
The settlement includes the transfer of shares from the seller’s account to the buyer’s account and the transfer of money from the buyer’s account to the seller’s account.
What is Legal Framework?
As we all know that all the buying and selling of shares in the stock market is done with the permission of the government of that nation. So, the process of buying and selling needs the issuance of government securities.
Some Key Terminologies that you should know
- Pay-in Day: The day in which the broker or trading member makes payment of funds or delivery of securities.
- Security Pay-in: The process of transfer of shares from the client’s company’s Demat account to the broker’s account.
- Funds Pay-in: The process of transfer of funds to the clearing corporation account
- Pay-out Day: The day in which the clearing corporation of the stock exchange transfer funds as well as securities to the trading member or broker’s account.
- Security Pay-out: The process of receiving securities from the clearing corporation to complete the settlement of the purchase transaction.
- Funds Pay-Out: Find the payout funds payout is the process of transfer of the funds from the clearing corporation.
What is a Transaction Table?
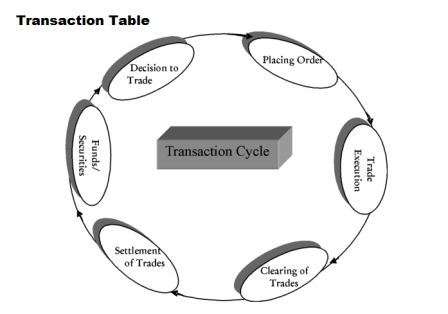
The transaction cycle shown in the above image help to learn the steps of transaction in stock markets. In it, you can learn about how the settlement and clearing are done along with some legal framework by the broker to satisfy clearing corporations as well as trade members in a short time period.
Steps in Transaction Cycle:
- In the above picture, we can see the transaction cycle. This cycle consists of five main steps. In the first step, a person executes a trade that may be securities or funds either to meet his liquidity needs or to reshuffle his holding in response to change in his perception about risk and return of the acids decides to buy/sell.
- In the second phase of the transaction cycle the person who selects a broker and instruct him to place it may be by or sold order on an exchange.
- After this in the third step the order is converted to a trade as soon as it finds a match for buying or selling order.
- At the end of the trade cycle the trades are needed to determine the obligation of the trading member to deliver securities or funds as per settlement schedule.
- In the last step of transaction cycle the buyer or seller delivers fund or securities and receives securities or refunds and squares ownership of the securities in IT are security transaction cycle is present.
Settlement Agencies:
There are several settlement agencies that play a vital role in the process of clearing and settling the trades executed on exchanges so some of them are given below with a brief description about them.
1. Clearing Corporation (NSCCL): The term NSCCL stands for National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited. The National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited or NSCCL is responsible for post-trade activities of any stock exchange.
The Clearing and settlement of trades and risk management are central functions of National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited.
The NSCCL clears all trades, determines obligations of members, arranges for pay-in of receives funds/securities, funds/securities, processes for shortages in funds/securities, guarantees settlement, arranges for pay-out of funds/securities to members, and collects and maintains margins/collateral/base capital/other funds.
2. Custodians: A custodian is a kind of entity that is responsible for safeguarding the documentary evidence of the title to property like share certificates etc. The titles to the custody property remain vested with the original holders or in their nominees or custodian trustee.
The NSCCL custodian is a clearing member but not a trading member. The custodian basically helps in settling trades assigned by trading members. They are made required to confirm whether it is going to settle a particular trade or not.
Once it is confirmed, the NSCCL assigns that obligation to that custodian and the custodian is required to settle it on the settlement day. If the custodian rejects the trade, the obligation is assigned back to the trading/clearing members.
3. Clearing Members: The Clearing Members are responsible for settling their obligations as determined by the National Securities Clearing Corporation Limited (NSCCL).
Basically, the Clearing Members have to make available funds/securities in the designated accounts with clearing depository/bank participants, as the case may be, to meet their obligations on the settlement day.
In the capital market segment, all the trading members of the Exchange are required to become the Clearing members of the Clearing Corporation.
4. The Clearing Banks: Clearing banks play a key link between the clearing members and the NSCCL for the settlement of funds. Every clearing member is required to open a dedicated settlement account with one of the clearing banks.
The clearing member makes funds available in the clearing account for the pay-in on the pay-in day and receives funds in case of a pay-out on the pay-out day. There are some main functions that are performed by the Clearing Banks. So, the main function of Clearing Banks are given below:
(a) Branch network in cities that cover bulk of the trading cum clearing members
(b) High level of automation including Real-time gross settlement (RTGS) as well as electronic funds transfer (EFT) facilities.
(c) Facilities such as dedicated branch facilities and software to interface with the clearing corporation along with access to account information on a real-time basis.
(d) Value-added services to members such as free-of-cost funds transfer across centers etc.
(e) The Clearing Banks help in providing working capital funds.
(f) Works in the services as Depository Participants (an agent of the depository through which it interfaces with the investor).
(h) The Clearing Banks help in some other Capital Market related facilities.
(i) All other banking facilities like issuing bank guarantees/credit facilities etc.
5. Depository: A depository is a kind of entity where the securities of any investor are held in electronic form. The person who holds a Demat account is called the beneficiary owner. In the case of a joint account, the account holders are beneficiary holders of that joint account.
The Depositories help in the settlement of the dematerialized securities. The depository runs an electronic file to transfer the securities from accounts of the custodians or clearing members to that of the NSCCL.
As per the schedule of allocation of securities determined by the NSCCL, the depositories transfer the securities on the pay-out day from the account of the NSCCL to those of the trading members or custodians.
Clearing and Settlement Process
Here we are going to tell you about the Clearing and Settlement procedure in short. We hope that you found Financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes very helpful and interesting. So, continue your studies with our notes.
In the process of clearing and settlement of any trade, the NSCCL becomes the legal counterparty to the net settlement obligation of every member. This principle is also called ‘Novation’. In case a member fails on any obligation, the NSCCL immediately cuts off trading and initiates recovery on that trading member.
Clearing Process
The clearing process includes the updating of the accounts of trading parties and arrangements for the transfer of money as well as securities.
Settlement Process
The settlement process involves the actual exchange of money or some other value for the securities.
Steps of Settlement Process
1. Pay-in of Funds and Securities: First of all the trading member brings the funds/securities available in their designated accounts of Pay-in of Funds and Securities:
First of all the trading member brings the funds/securities available in their designated accounts of depositories by the pay-in time.
Then the depositories move the securities that are available in trading member’s accounts to the NSCCL.
After this transfer, the NSCCL sends electronic instructions to the clearing Bank to debit the member’s account and credit account of NSCCL.
2. Pay-out of Funds and Securities: After processing the shortage of funds/securities and arranging for the movement of funds from surplus banks through RBI clearing, the NSCCL sends electronic instructions to the depositories for clearing banks to debit accounts of NSCCL and credit settlement accounts of trading members.
We would like to suggest you read financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes very carefully to understand each and every topic clearly. And we had already published notes for financial marketing management class 12 notes of all chapters.
So, you can read them too. The links to these chapters are given at the bottom of this article.
You should also read the financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes and other chapters notes are given below. You just have to click on them to read the notes:
- Financial markets management class 12 chapter 1 notes
- Financial markets management class 12 chapter 2 notes
- Financial markets management class 12 chapter 3 notes– This is given in this article.
- Financial markets management class 12 chapter 4 notes
- Financial markets management class 12 chapter 5 notes
